Trends in Current Use of HNB Tobacco / E-Cigarette, Both Sexes, Japan
Knowledge•Action•Change (2018)Takahiro Tabuchi , Silvano Gallus , Tomohiro Shinozaki , Tomoki Nakaya , Naoki Kunugita , Brian Colwell
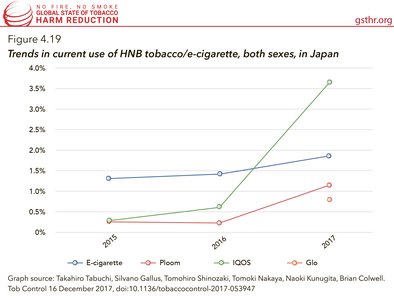
Surveys of the adult population show the initial uptake of heat-not-burn (HNB) devices in Japan. In 2015, 1.3 percent of adults were using e-cigarettes (despite their illegality) but only 0.3 percent were currently using IQOS and 0.3 percent Ploom TECH HNB devices. One year later, in 2016, these levels had not changed greatly. By 2017, e-cigarette use had increased to 1.9 percent, while use of IQOS had increased to 3.6 percent, use of Ploom TECH increased to 1.2 percent, and use of the glo HNB product was 0.8 percent. The other sources of information about HNB come from market data. Philip Morris International’s (PMI) IQOS uses ‘HeatSticks’ which accounted for 0.4 percent of the tobacco product market in December 2015, rising to a 14.1 percent share of the tobacco market by December 2017.56 In two years, IQOS has overtaken specific cigarette brands – for example PMI’s own Marlboro which has about eight percent of the tobacco market.
The other sources of information about HNB come from market data. PMI’s IQOS uses ‘HeatSticks’ which accounted for 0.4 percent of the tobacco product market in December 2015, rising to a 14.1 percent share of the tobacco market by December 2017. In two years, IQOS has overtaken specific cigarette brands – for example PMI’s own Marlboro which has about eight percent of the tobacco market.
See also p. 55 of the report: No Fire, No Smoke: The Global State of Tobacco Harm Reduction 2018 — Global State of Tobacco Harm Reduction (gsthr.org)
Trends in Current Use of HNB Tobacco / E-Cigarette, Both Sexes, Japan