Difference Between Levels of Adult Tobacco Smoking for Males and Females
Difference Between Levels of Adult Tobacco Smoking for Males and Females
Knowledge•Action•Change (2020)- Burning Issues: The Global State of Tobacco Harm Reduction 2020
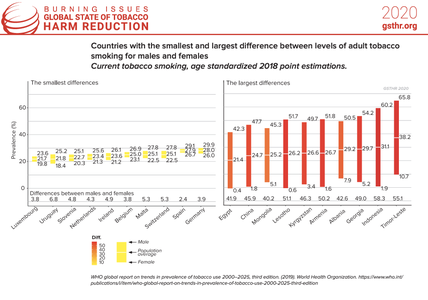
Average levels of smoking at a national level hide significant differences in the levels of smoking between males and females. Almost one third of men (30%) globally smoke compared with 10% of women.
According to WHO data for 2018, the prevalence of current tobacco smoking among men in 35 countries is above 40%. This ranges from a staggering 69% in Kiribati, to 50% in in Albania, Cyprus, Kyrgyzstan and Latvia, 45% in Greece, Mongolia and Republic of Moldova and 41% in Ukraine, the Russian Federation, Bangladesh and Samoa, as shown in this infographic.
In a few high-prevalence countries, the level of female smoking is higher than the male smoking levels found in lower prevalence countries for example, in Kiribati, Nauru, Chile and Serbia, over 40% of women smoke compared to 78 other countries where less than 30% of men smoke.
In some indigenous communities, such as the Māori, more women smoke than men (see Chapter 7 of the report: Burning Issues: The Global State of Tobacco Harm Reduction 2020) . There is some evidence that for cultural or social reasons in some countries, there may be under-reporting of female smoking.
See also p.30 of the report: Burning Issues: The Global State of Tobacco Harm Reduction 2020